Nginx之Location配置详解(Location匹配顺序)
location有”定位”的意思,主要是根据uri来进行不同的定位。在虚假主机的配置中,是必不可少的。
location可以把网站的不同部分,定位到不同的处理方式上。
一、location的基础语法
1 | location [=|~|~*|^~] /uri/ { … } |
二、location如何发挥作用
本章以192.168.60.106为例
1、精准匹配和一般匹配
1 | location = /zg/ { |
请求URL:http://192.168.60.106/zg/ 访问时匹配的是:=/zg/
2、精准匹配和一般匹配,uri后面不带“/”匹配
1 | location = /zg { |
请求URL:http://192.168.60.106/zg/ 访问时匹配的是:/zg
3、精准匹配和一般匹配,uri前面和后面都不带“/”
1 | location = zg { |
请求URL:http://192.168.60.106/zg/ 访问时匹配的是:= zg
4、精准匹配和一般匹配,uri带”/“和不带”/“匹配
1 | location = zg { |
请求URL:http://192.168.60.106/zg/ 访问时匹配的是:/zg/ 顺序换也是一样
综上所述:路径相同时的精准匹配优先,必须是满足/uri/或者uri,要么uri两加都加/,要么uri两边都不加斜杆的情况
5、一般匹配时的匹配规则
1 | location /images/ { |
在html下创建file,lfile文件夹,然后在file下创建images文件夹,在images下创建aa文件夹,在lfile下创建images文件夹,接着在images下创建aa文件夹,然后同时在两个aa文件夹下导入test.jpg图片,这样file和lfile下都有images/aa路径
请求url:http://192.168.60.106/images/aa/test.jpg,既能匹配/images/,又能匹配/images/aa,这时以最长uri匹配优先,匹配的是:/images/aa
6、^~开头的非正则匹配和一般匹配
^~代表非正则匹配,非正则,不需要继续正则匹配。
1 | location ^~ /images/ { |
^~:如果这个匹配使用^〜前缀,搜索停止。这个前缀官网和网上都说得很含糊,加上这个前缀,是会停止搜索正则匹配,但是想对一般匹配是不会停止的,也就是说还是可以匹配到一般匹配的。
请求url: http://192.168.60.106/images/aa/test.jpg,匹配结果:/images/aa/
7、^~开头的非正则匹配和正则匹配
~ 开头表示区分大小写的正则匹配
1 | location ^~ /images/ { |
请求url: http://192.168.60.106/images/aa/test.jpg,匹配结果:^~/images/
8、严格精准匹配和正则匹配
1 | location / { |
严格精准匹配,如果被严格精准匹配到了,则不会继续搜索正则匹配
如果http://192.168.60.106,这个就严格精准匹配到了 /,则不会继续匹配 ~ .html$
如果:http://192.168.60.106/index.html,则会被/ 匹配到,但是不是严格精准匹配,则会继续搜索正则匹配
9、正则匹配规则
都是正则uri的情况下,匹配是按照编辑顺序的
1 | location ~ \.html$ { |
请求URL:http://192.168.60.106/prefix/index.html,会优先匹配前面定义的location。
10、@开头的uri
1 | error_page 404 = @fallback; |
@开头的,如果请求的 URI 存在,则本 nginx 返回对应的页面;如果不存在,则把请求代理到baidu.com 上去做个弥补,其实就是做了一个容错,把找不到的url全部转发到fallback的反向代理服务器去。
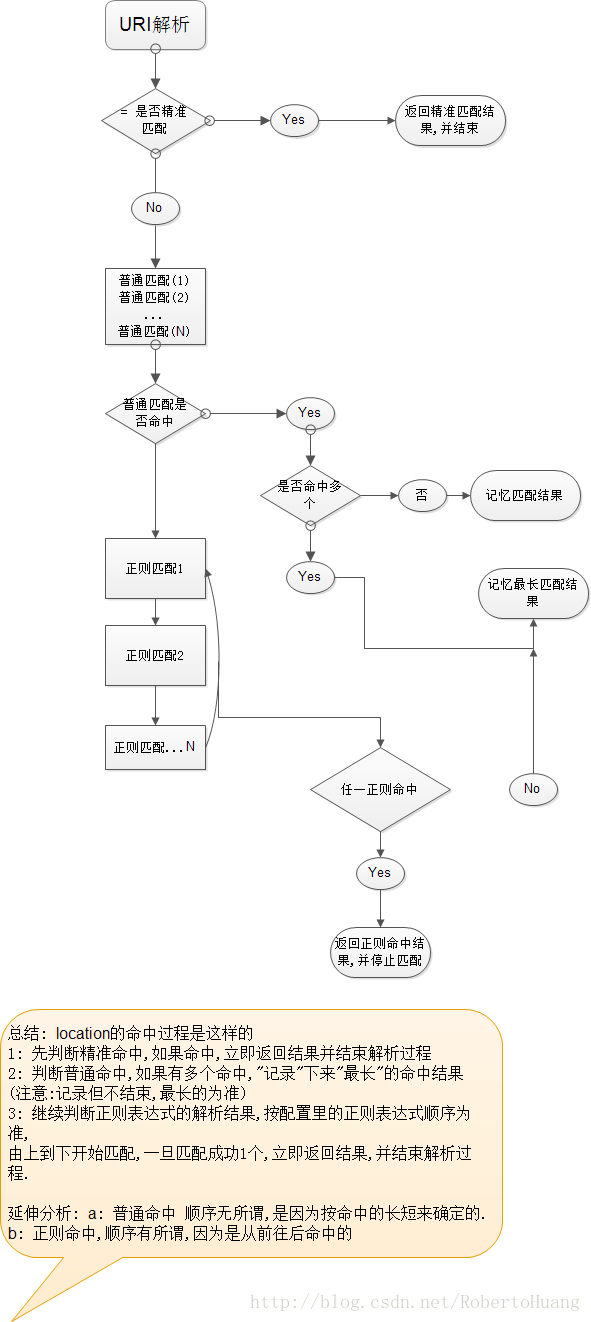
最后总结:
- 先判断精准命中,如果命中,立即返回结果并结束解析过程
- 判断普通命中,如果有多个命中,记录下来最长的命中结果
3、如果是^~开头的命中,则不会继续搜索正则命中,但是会继续搜索一般命中
- 继续判断正则表达式的解析结果,按配置里的正则表达式顺序为准,由上到下开始匹配,一旦匹配成功立刻返回结果,并结束解析过程。
延伸分析:a. 普通命中:顺序无所谓,是因为按命中长短来确定的 b. 正则命中:顺序有所谓,因为是从前往后命中的
原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/luoyang_java/article/details/83507193